[ad_1]
Given that Windows is not one of the most stable operating systems for desktops, it’s essential to know how to track a PC’s startup and shutdown history.
Checking the Startup and Shutdown History can help you find underlying issues and troubleshoot them effectively. Technicians can also ask you for this information to fix certain issues on your PC.
How to Check Your Startup and Shutdown History in Windows
So, whether you’re a pro Windows user or just a beginner, here are the best ways to check the Startup and Shutdown history on a Windows PC.
Important Event ID You Should Remember
Since we will be accessing the event log to check the Startup and shutdown history, you should note these Event IDs. This will help you pick the Startup and shutdown events more effectively.
Event ID 6005: This one is a startup identifier. If this appears, it means a system startup.
Event ID 6006: This one is used to identify system shutdown.
Event ID 6008: This is also a system shutdown identifier, but it signifies that your PC has shut down absurdly.
Event ID 6013: This Event ID shows your system uptime in seconds.
Event ID 41: This means your PC rebooted without shutting down completely.
Event ID 1074: This event appears when an app forces a system to restart or when the user restarts/shutdowns via the Start Menu.
Event ID 1076: This event details why your system was restarted or shutdown.
1. How to Check Startup and Shutdown History via Command Prompt
You can utilize the Command Prompt utility to check your PC’s Startup and Shutdown history. Here’s what you need to do.
1. Type Command Prompt in the Windows 11 Search. When the Command prompt appears, right-click on it and select Run as administrator.
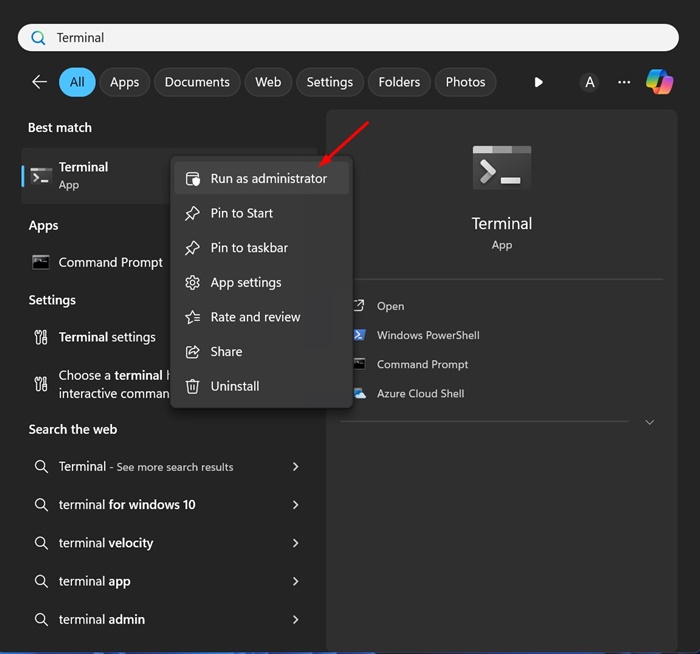
2. When the Command Prompt opens, execute this command:
wevtutil qe system “/q:*[System [(EventID=6006)]]” /rd:true /f:text /c:1
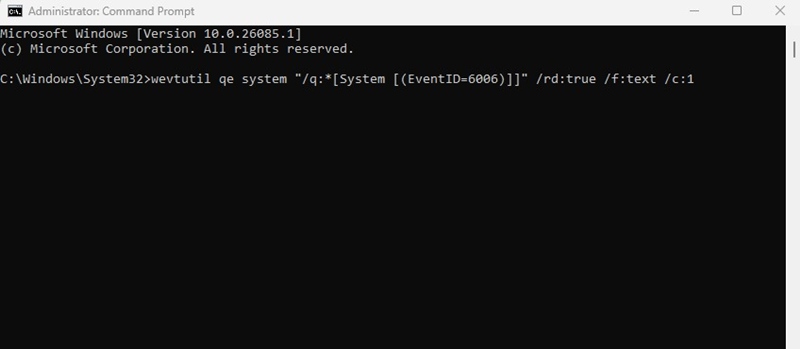
3. The command prompt will now show the shutdown activity.
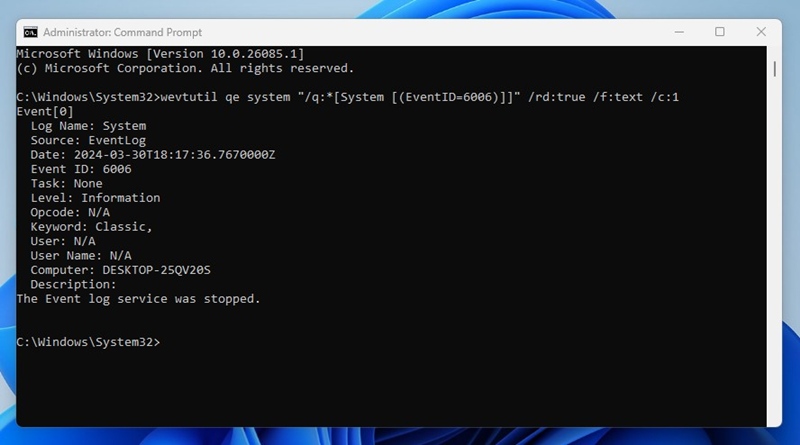
4. To view the startup activity, execute this command:
wevtutil qe system “/q:*[System [(EventID=6005)]]” /rd:true /f:text /c:1
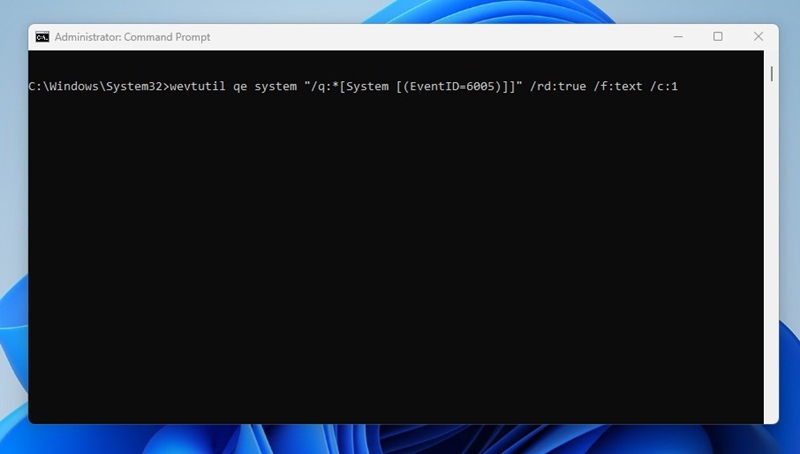
That’s it! This is how you can use the Command Prompt utility to check the Startup and Shutdown history on Windows 11.
2. Check the Startup and Shutdown History via Windows Event Viewer
Not everyone feels comfortable operating the Event Viewer Tool; for this reason only, we have kept this method at number 2. However, on Windows Event Viewer, you can keep track of all the Event IDs we shared with you above. Here’s what you need to do.
1. Type in Event Viewer on the Windows 11 Search. Next, open the Event Viewer app from the list of best match results.
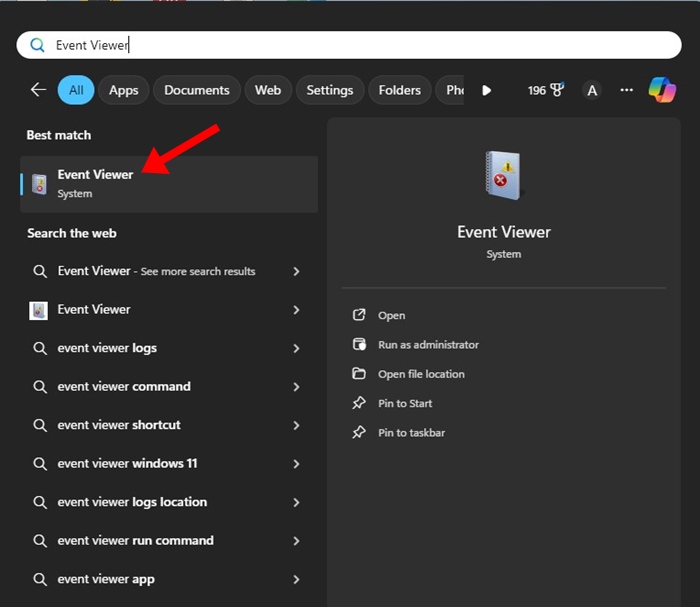
2. When the Event Viewer opens, switch to Windows Logs.
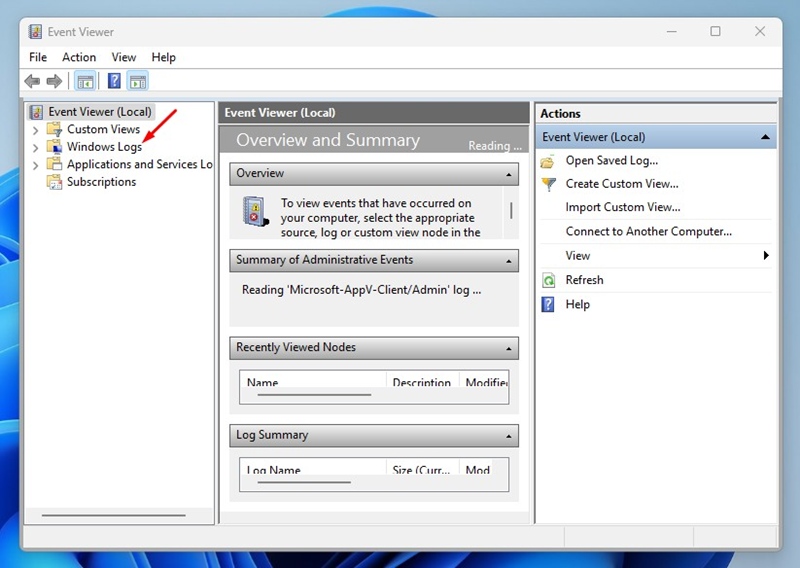
3. On the right side, double click on System.
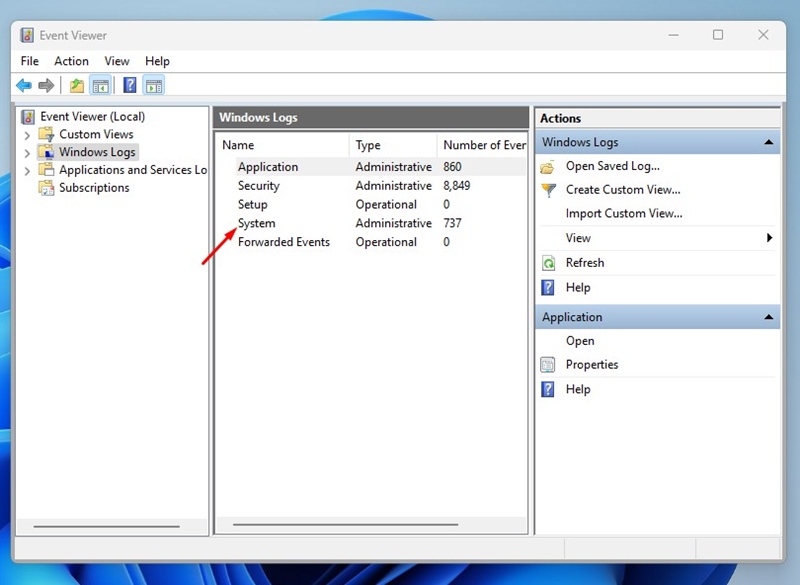
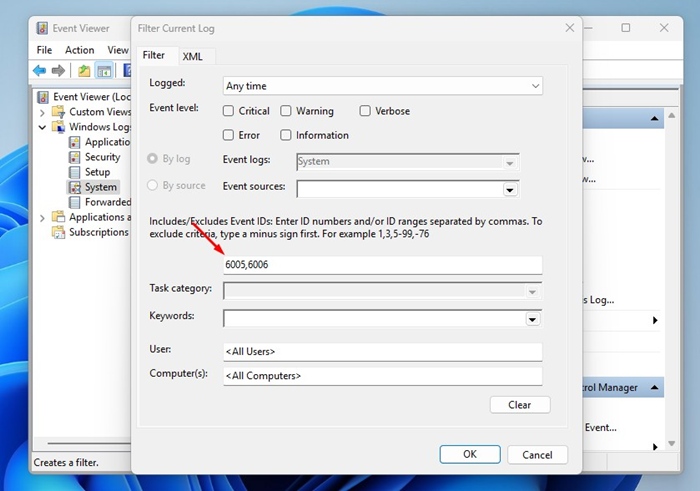
4. On the right pane, click on Filter Current Log.
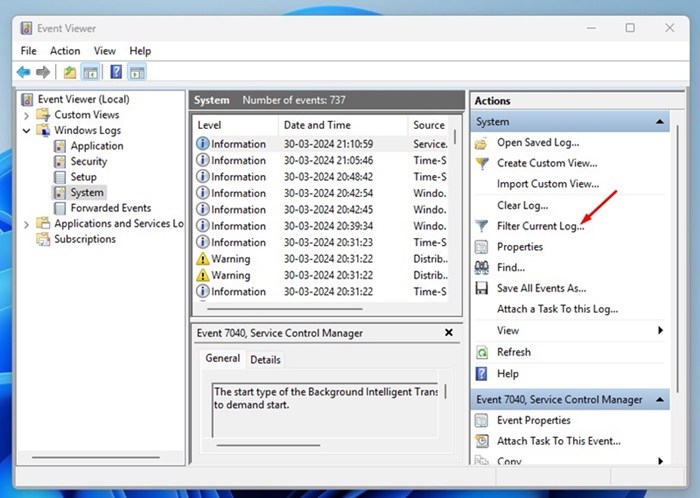
5. On the Filter Current Log prompt, enter 6005 and 6006 on the field shown in the screenshot and click OK.
6. Now, you will see many event logs. Each log indicates either a shutdown or a startup. You can double-click on the event logs to view more information.
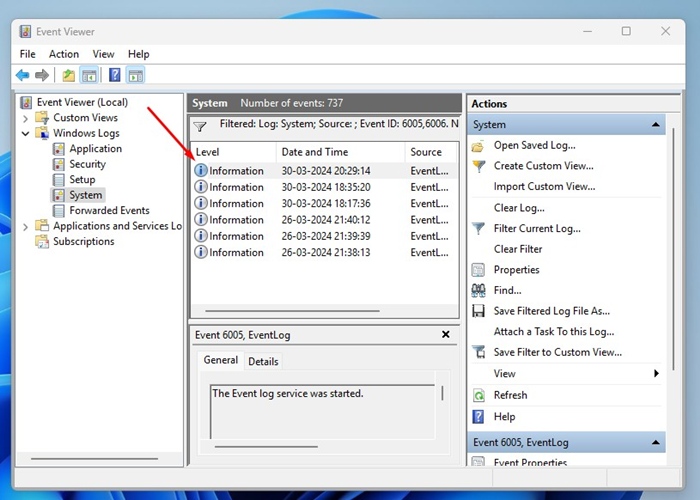
That’s it! This is how you can check the Windows Startup and Shutdown history via Windows Event Viewer.
3. View Startup & Shutdown History on Windows Using PowerShell
This method will use the PowerShell utility to check the Startup and Shutdown history. Here’s what you need to do.
1. Type in PowerShell on the Windows Search. Next, right click on the PowerShell and select Run as administrator.
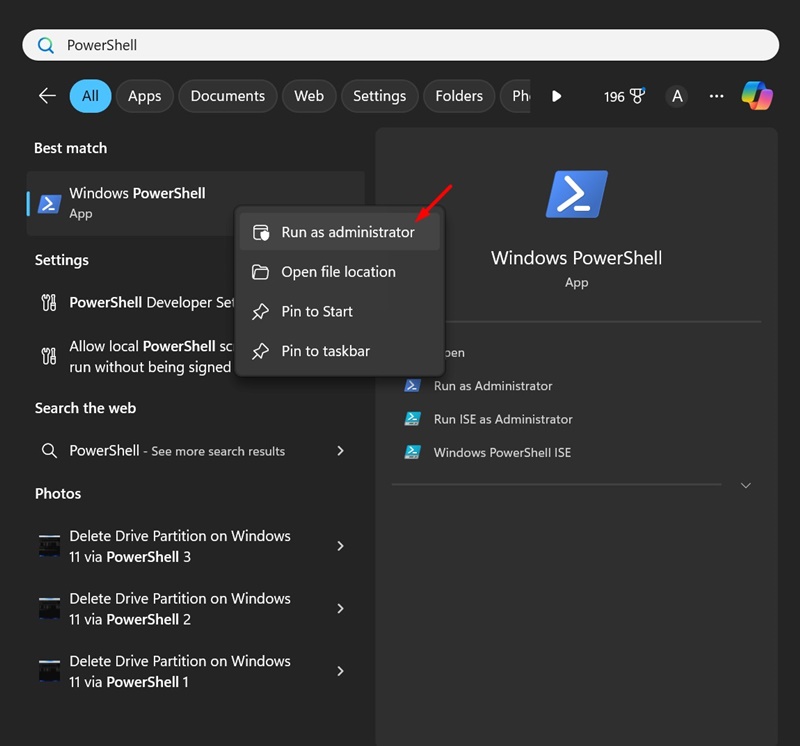
2. When the PowerShell opens, execute the given command:
Get-EventLog -LogName System |? {$_.EventID -in (6005,6006,6008,6009,1074,1076)} | ft TimeGenerated,EventId,Message -AutoSize -wrap
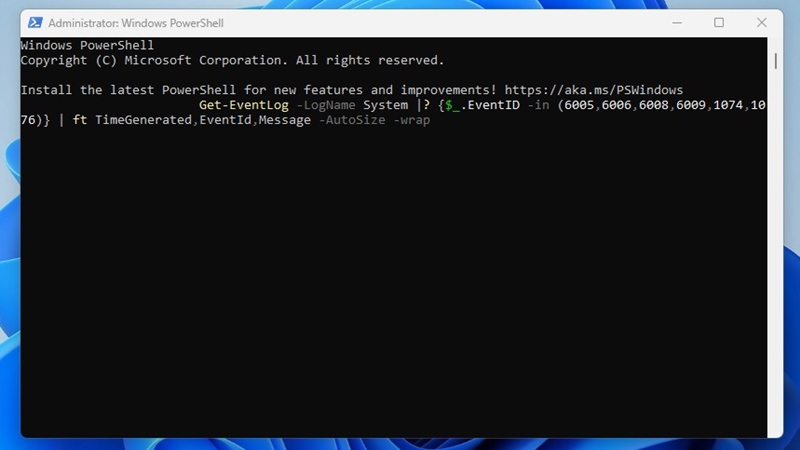
3. The PowerShell utility will return detailed information on the event codes you’ve entered in the command. The result will be divided into three columns: Time Generated, EventID, and Message.
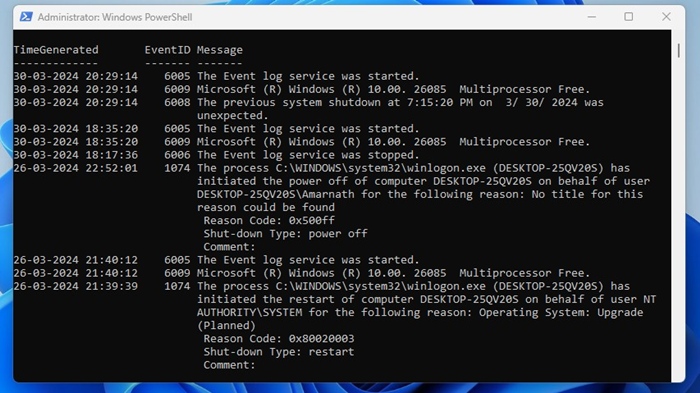
You need to analyze the information to find the history of the startup and shutdown.
This guide explains how to check the Startup and Shutdown history on a Windows PC. You can use this information to troubleshoot many PC issues. In the comments, let us know if you need more help on this specific topic. Also, if you find this guide helpful, don’t forget to share it with your friends.
[ad_2]
Source link
